

For each read in our reads data, STAR tries to find the longest possible sequence which matches one or more sequences in the reference genome. Many tools have been developed for read alignment, but today we will focus on STAR. Some form of alignment is generally required if we want to quantify gene expression or find genes which are differentially expressed between samples. Now we have established that our reads are of good quality, we would like to map them to a reference genome. open a terminal, cd to the docer folder (the folder you downloaded from github) and run this command: The cells were sequenced using the SMART-seq2 library preparation protocol and the reads are paired end.įirst, let’s open the docker in a bash mode. Today we will be performing our analysis using a single cell from an mESC dataset produced by (Kolodziejczyk et al. 2015), which you downloaded froom the github link. Now let’s make a FastQC report ourselves.
This gives an example of what an ideal report should look like for high quality Illumina reads data. Scroll down the webpage to ‘Example Reports’ and click ‘Good Illumina Data’. Fortunately we have already installed FastQC for you today, so instead we will take a look at the documentation.
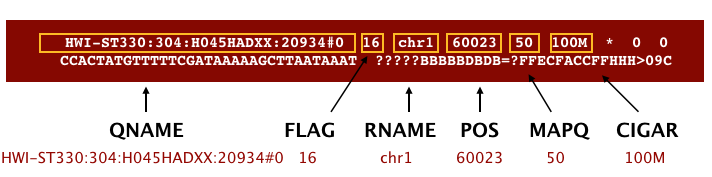
#Bam file format columns install
This website contains links to download and install FastQC and documentation on the reports produced. Copy and paste this link into your browser to visit the FastQC website: FastQC takes sequencing data as input and returns a report on read quality. FastQC is a quality control tool for sequencing data, which can be used for both bulk and single-cell RNA-seq data. For this task, today we will be using a tool called FastQC. Once you’ve obtained your single-cell RNA-seq data, the first thing you need to do with it is check the quality of the reads you have sequenced.
19.1 Comprehensive list of single-cell resources.16.8 Additional exploration: another example of multi-modal analysis.16.7 Cluster directly on protein levels.16.6 Identify differentially expressed proteins between clusters.16.5 Visualize protein levels on RNA clusters.16.4 Add the protein expression levels to the Seurat object.16.3 Setup a Seurat object, and cluster cells based on RNA expression.14.8 Plots of gene expression over time.14.7 Comparison of the different trajectory inference methods.14.2 First look at the differentiation data from Deng et al.12.5 Additional exploration: Regressing out unwanted covariates.12.4.2 Batch correction: integrative non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) using LIGER.12.4.1 Batch correction: canonical correlation analysis (CCA) + mutual nearest neighbors (MNN) using Seurat v3.12.4 Cluster pancreatic datasets without batch correction.12.3 Preparing the individual Seurat objects for each pancreas dataset without batch correction.12.2 Read in pancreas expression matrices.10.3.1 Differential Expression Analysis.10.2.3 Run non-linear dimensional reduction (UMAP/tSNE).10 Feature Selection and Cluster Analysis.8.7 Detection of variable genes across the single cells.8.6.1 Preprocessing step 2 : Expression normalization.8.5 Preprocessing step 1 : Filter out low-quality cells.8.3.2 Plot cells ranked by their number of detected genes.8.3.1 Look at the summary counts for genes and cells.8.2.5 How much memory does a sparse matrix take up relative to a dense matrix?.8.2.3 Let’s examine the sparse counts matrix.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
